Research and develop smart health solutions to provide widelyaccessible monitoring, screening, and diagnostics for peopleall over the world.
Read More
Research and develop smart health solutions to provide widelyaccessible monitoring, screening, and diagnostics for peopleall over the world.
Read More
Research and develop smart health solutions to provide widelyaccessible monitoring, screening, and diagnostics for peopleall over the world.
Read More
Research and develop smart health solutions to provide widelyaccessible monitoring, screening, and diagnostics for peopleall over the world.
Read More
Research and develop smart health solutions to provide widelyaccessible monitoring, screening, and diagnostics for peopleall over the world.
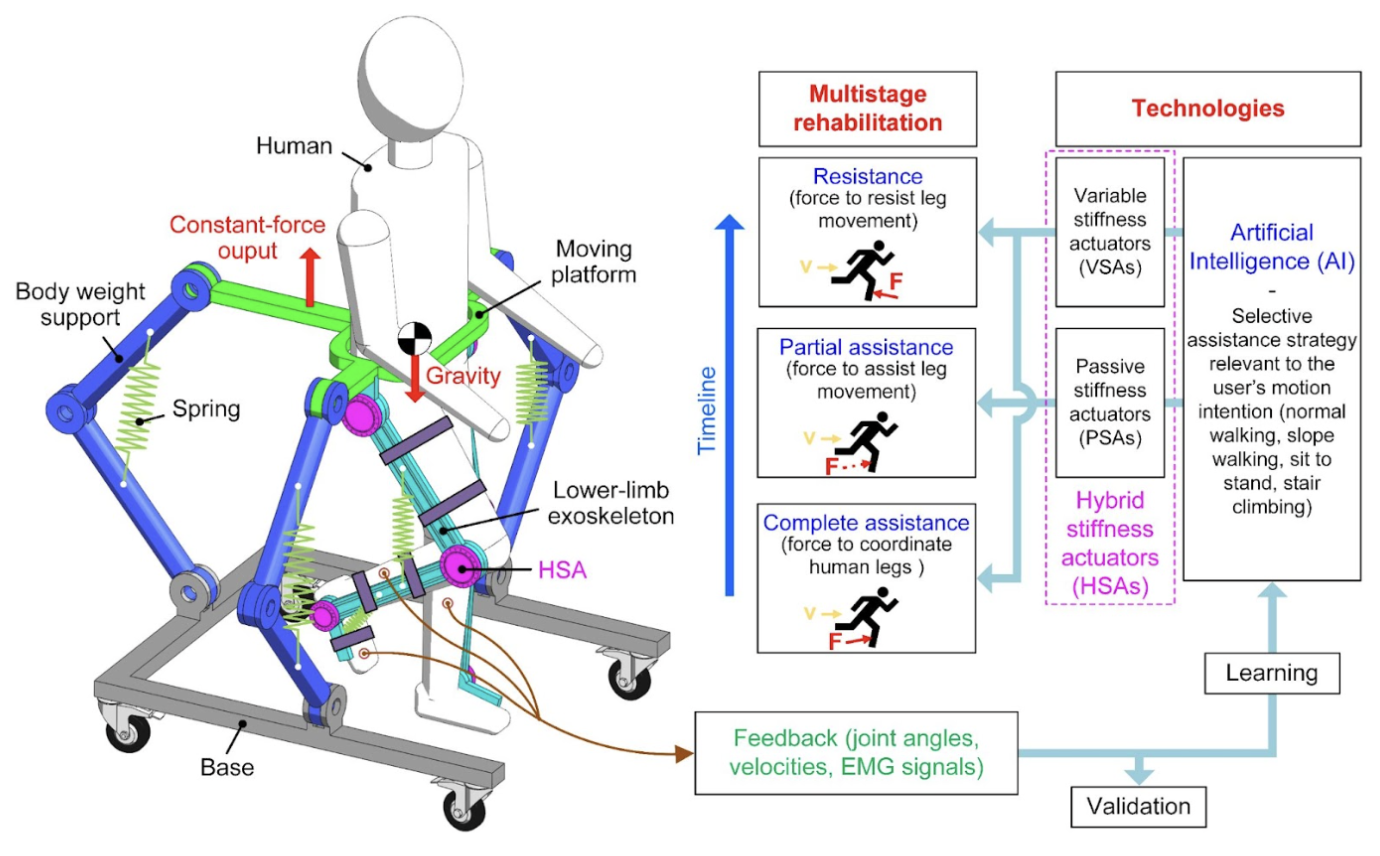
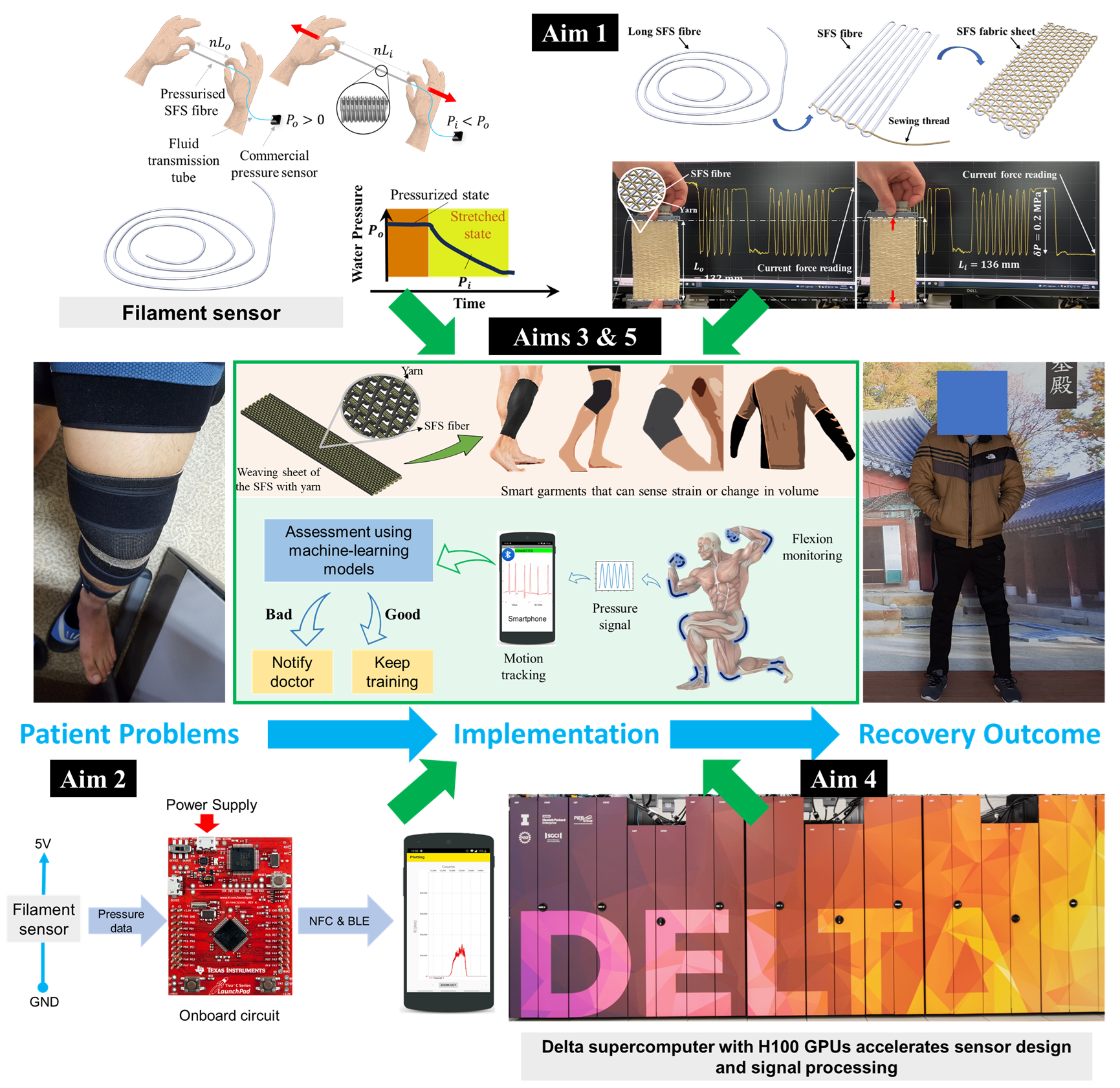
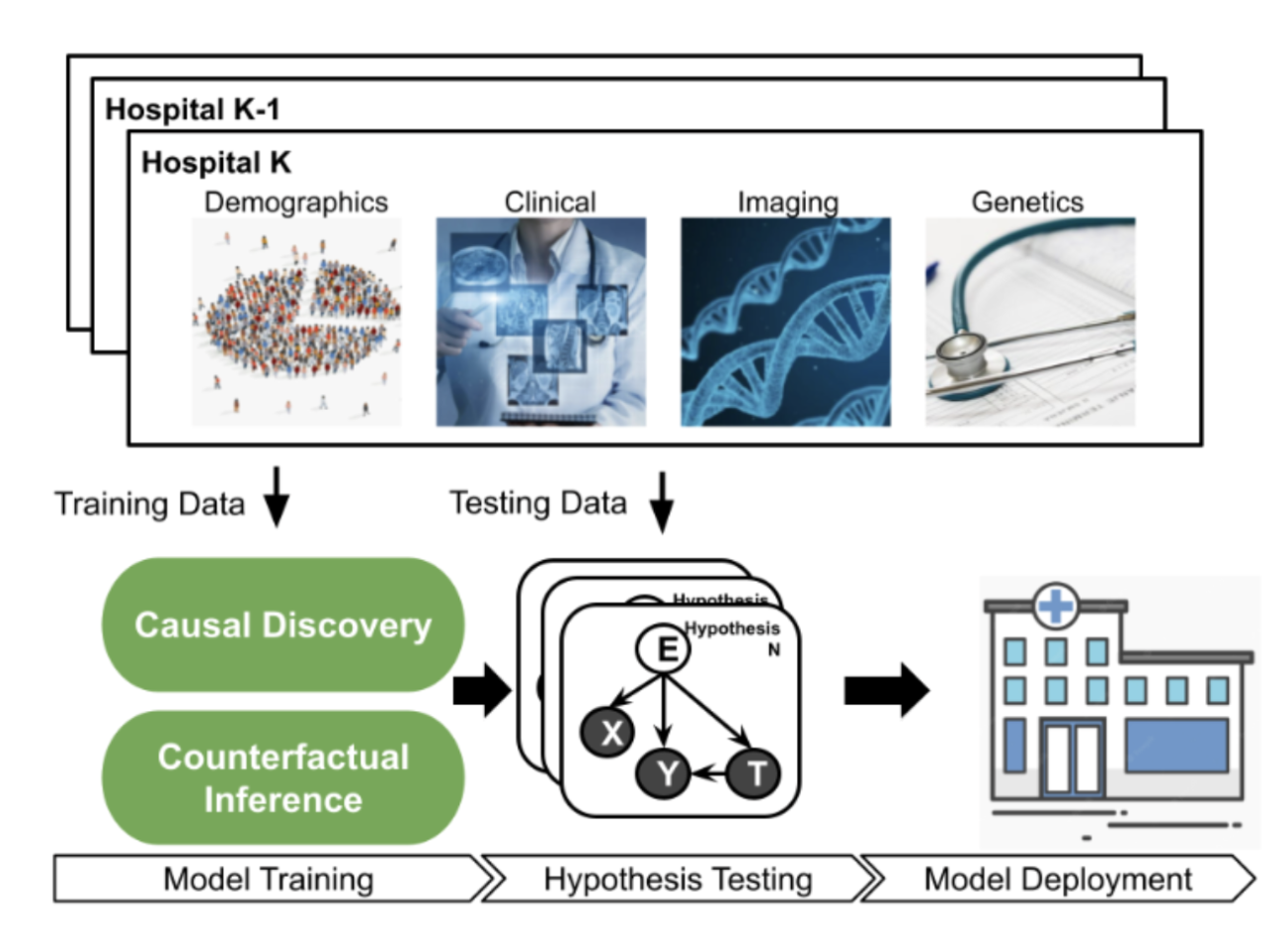
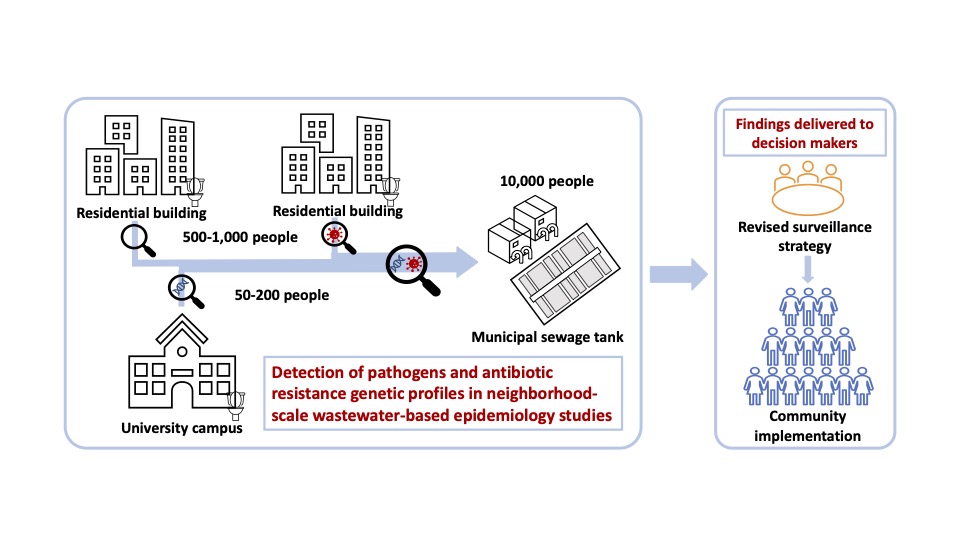
Read MoreThe VinUni-Illinois Smart Health Center (VISHC) is a collaboration between VinUniversity (VinUni) and the Grainger College of Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC or Illinois). The center was established to conduct high-impact research on biomedical sensing, informatics, and their applications in smart healthcare. We aim at developing state-of-the-art sensing and digital technologies to provide widely accessible health monitoring and improvement for people all over the world.





Director
Honorary Vice Provost, VinUniversity Professor, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, UIUC
View profile
Associate Director
Associate Director of VISHC Assistant Professor, College of Engineering & Computer Science (CECS), VinUniversity
View profile
VISHC Scientific Director
Ivan Racheff Professor of Environmental Engineering in CEE, UIUC CEE Excellence Faculty Fellow
View profile
Center Manager
VinUni-Illinois Smart Health Center VinUniversity

Lab Manager & Research Fellow
VinUni-Illinois Smart Health Center
View profile